
Over 2 million + professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Unlock the essentials of corporate finance with our free resources and get an exclusive sneak peek at the first module of each course. Start Free
A callable bond (redeemable bond) is a type of bond that provides the issuer of the bond with the right, but not the obligation, to redeem the bond before its maturity date. The callable bond is a bond with an embedded call option.
These bonds generally come with certain restrictions on the call option. For example, the bonds may not be able to be redeemed in a specified initial period of their lifespan. In addition, some bonds allow the redemption of the bonds only in the case of some extraordinary events.

Callable bonds may be beneficial to the bond issuers if interest rates are expected to fall. In such a case, the issuers may redeem their bonds and issue new bonds with lower coupon rates.
On the other hand, callable bonds mean higher risk for investors. If the bonds are redeemed, the investors will lose some future interest payments (this is also known as refinancing risk). Due to the riskier nature of the bonds, they tend to come with a premium to compensate investors for the additional risk.
Generally, the majority of callable bonds are municipal or corporate bonds.
To understand the mechanism of callable bonds, let’s consider the following example.
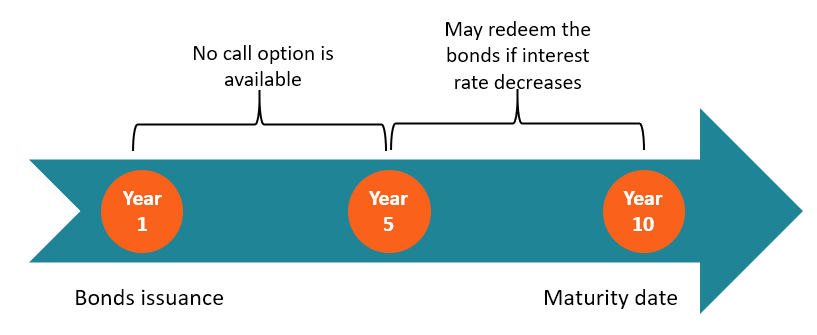
ABC Corp. issues bonds with a face value of $100 and a coupon rate of 6.5% while the current interest rate is 4%. The bonds will mature in 10 years.
However, the company issues the bonds with an embedded call option to redeem the bonds from investors after the first five years.
If interest rates have declined after five years, ABC Corp. may call back the bonds and refinance its debt with new bonds with a lower coupon rate. In such a case, the investors will receive the bond’s face value but will lose future coupon payments.
However, if the interest rate increases or remains the same, there is no incentive for the company to redeem the bonds and the embedded call option will expire unexercised.
Valuing callable bonds differs from valuing regular bonds because of the embedded call option. The call option negatively affects the price of a bond because investors lose future coupon payments if the call option is exercised by the issuer.
The value of a callable bond can be found using the following formula:

CFI offers the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following resources will be helpful: